Industrial Electronics Career Information and Requirements
miércoles, 21 de junio de 2017
miércoles, 14 de junio de 2017
🔻WHEN DID ROBOTS, AS WE KNOW THEM TODAY, COME INTO EXISTENCE?
The first industrial modern robots were the Unimates
developed by George Devol and Joe Engelberger in the late 50's and early 60's.
The first patents were by Devol for parts transfer machines. Engelberger formed
Unimation and was the first to market robots. As a result, Engelberger has been
called the 'father of robotics.'
Modern industrial arms have increased in capability and performance through controller and language development, improved mechanisms, sensing, and drive systems. In the early to mid 80's the robot industry grew very fast primarily due to large investments by the automotive industry. The quick leap into the factory of the future turned into a plunge when the integration and economic viability of these efforts proved disastrous. The robot industry has only recently recovered to mid-80's revenue levels. In the meantime there has been an enormous shakeout in the robot industry. In the US, for example, only one US company, Adept, remains in the production industrial robot arm business. Most of the rest went under, consolidated, or were sold to European and Japanese companies.


🔻HOW DO ROBOTS EXPLORE OTHER WORLDS?
Robots help explore space. Spacecraft that explore other worlds, like the moon or Mars, are robots. These include orbiters, landers and rovers on other planets. The Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity are robots. Other robotic spacecraft fly by or orbit other worlds. These robots study planets from space. The Cassini spacecraft is this type of robot. Cassini studies Saturn and its moons and rings. The Voyager and Pioneer spacecraft are now traveling beyond our solar system. They are also robots. People use computers to send messages to the spacecraft. The robots have antennas that pick up the message commands. Then the robot does what the person has told it to do.
ROBOTICS
Robotics is a branch of engineering that involves the conception, design, manufacture, and operation of robots. This field overlaps with electronics, computer science, artificial intelligence, mechatronics, nanotechnology and bioengineering.
🔻WHERE DID THE WORD 'ROBOT' COME FROM?
The word 'robot' was coined by the Czech playwright Karel Capek (pronounced "chop'ek") from the Czech word for forced labor or serf. Capek was reportedly several times a candidate for the Nobel prize for his works and very influential and prolific as a writer and playwright. Mercifully, he died before the Gestapo got to him for his anti-Nazi sympathies in 1938.
The use of the word Robot was introduced into his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots) which opened in Prague in January 1921. The play was an enormous success and productions soon opened throughout Europe and the US. R.U.R's theme, in part, was the dehumanization of man in a technological civilization. You may find it surprising that the robots were not mechanical in nature but were created through chemical means.

The term 'robotics' refers to the study and use of robots. The term was coined and first used by the Russian-born American scientist and writer Isaac Asimov (born Jan. 2, 1920, died Apr. 6, 1992). Asimov wrote prodigiously on a wide variety of subjects. He was best known for his many works of science fiction. The most famous include I Robot (1950), The Foundation Trilogy (1951-52), Foundation's Edge (1982), and The Gods Themselves (1972), which won both the Hugo and Nebula awards.
The word 'robotics' was first used in Runaround, a short story published in 1942. I, Robot, a collection of several of these stories, was published in 1950. Asimov also proposed his three "Laws of Robotics", and he later added a 'zeroth law'.
👉LAW
ZERO:A robot may not injure humanity, or, through inaction, allow humanity to come to harm.
👉LAW ONE:A robot may not injure a human being, or, through inaction,
allow a human being to come to harm, unless this would violate a higher order
law.
👉LAW TWO: A robot must obey orders given it by human beings, except
where such orders would conflict with a higher order law.
👉LAW THREE:A robot must protect its own existence as long as such
protection does not conflict with a higher order law.
Recuperado de :http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/robotics
Recuperado de:http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~chuck/robotpg/robofaq/1.html
martes, 6 de junio de 2017
THE
STORY OF ELECTRONICS
HISTORY OF ELECTRONICS DATES BACK TO 600 BC:
Let us now have a look at the timeline of discoveries and inventions in the field of electronics and electrical engineering from 600 BC to 2007:
💗1600 – William Gilbert coined the word electricus that was later termed as Electricity by Benjamin Franklin in 1752.
💗1720 – Stephen Gray discovered insulator and conductor.
💗1745 – Ewald Georg von Kleist and Pieter van Musschenbroek invented Leyden jars.
💗1752 – Benjamin Franklin discovered that lightning is electrical by flying a kite, and explained how Leyden jars work.
💗1783 – Charles Augustin de Coulomb formulated Coulomb’s law.
💗1800 – Alessandro Volta invented battery (Dry Cell).
💗1820 – Hans Christian Orsted discovered magnetic field.
💗1820 – André Marie Ampère published his law of electrodynamics called Ampère’s law.
💗1825 – William Sturgeon developed the first electromagnet.
💗1826 – Georg Ohm introduced Ohm’s Law.
💗1827 – Georg Ohm introduced the concept of electrical resistance.
💗1831 – Michael Faraday published the law of induction.
💗1931 – Michael Faraday invented transformer.
💗1831 – Joseph Henry developed a prototype DC motor.
💗1836 – Nicholas Callan invented transformer.
💗1844 – Samuel Morse developed telegraphy and the Morse code.
💗1856 – Charles Bourseul proposed telephony.
💗1862 – James Clerk Maxwell published four equations bearing his name “Maxwell’s equations”.
💗1876 – Alexander Graham Bell invented telephone.
💗1877 – Thomas Alva Edison invented phonograph.
💗1878 – Joseph Swan invented Incandescent light bulb.
💗1879 – Thomas Alva Edison introduced a long lasting filament for incandescent lamp.
💗1888 – Heinrich Hertz proved that electro magnetic waves travel over some distance.
💗1890 – Thomas Alva Edison invented fuse.
💗1897 – Karl Ferdinand Braun invented cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO).
💗1901 – Guglielmo Marconi made first transatlantic radio broadcast.
💗1904 – John Ambrose Fleming invented diode.
💗1906 – Lee de Forest invented triode.
💗1912 – Edwin Howard Armstrong developed Electronic oscillator.
💗1928 – First experimental Television broadcast in the US.
💗1929 – First public TV broadcast in Germany.
💗1941 – Konrad Zuse developed the first programmable computer.
💗1943 – Eisler invented the Printed Circuit Board.
💗1944 – John Logie Baird developed the first color picture tube.
💗1958 – Jack Kilby invented the integrated circuit (IC).
💗1960 – Theodore Harold Maiman invented the Laser.
💗1962 – Nick Holonyak Jr. invented the LED.
💗1962 – Hofstein, Heiman, and RCA invented MOSFET Transistors.
💗1964 – Kemeny and Kurtz introduced the BASIC programming language.
💗1970 – INTEL introduced the first Microprocessor.
💗1973 – John F. Mitchell and Dr. Martin Cooper of Motorola invented the first mobile phone.
💗2007 – Apple introduced the first iPhone.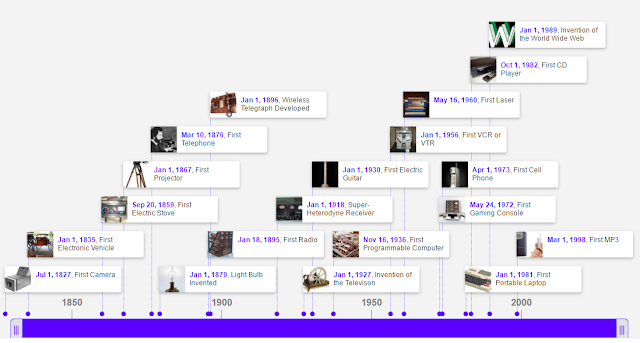
💗1720 – Stephen Gray discovered insulator and conductor.
💗1752 – Benjamin Franklin discovered that lightning is electrical by flying a kite, and explained how Leyden jars work.
💗1783 – Charles Augustin de Coulomb formulated Coulomb’s law.
💗1800 – Alessandro Volta invented battery (Dry Cell).
💗1820 – Hans Christian Orsted discovered magnetic field.
💗1820 – André Marie Ampère published his law of electrodynamics called Ampère’s law.
💗1825 – William Sturgeon developed the first electromagnet.
💗1826 – Georg Ohm introduced Ohm’s Law.
💗1827 – Georg Ohm introduced the concept of electrical resistance.
💗1831 – Michael Faraday published the law of induction.
💗1931 – Michael Faraday invented transformer.
💗1831 – Joseph Henry developed a prototype DC motor.
💗1836 – Nicholas Callan invented transformer.
💗1844 – Samuel Morse developed telegraphy and the Morse code.
💗1856 – Charles Bourseul proposed telephony.
💗1862 – James Clerk Maxwell published four equations bearing his name “Maxwell’s equations”.
💗1876 – Alexander Graham Bell invented telephone.
💗1877 – Thomas Alva Edison invented phonograph.
💗1878 – Joseph Swan invented Incandescent light bulb.
💗1879 – Thomas Alva Edison introduced a long lasting filament for incandescent lamp.
💗1888 – Heinrich Hertz proved that electro magnetic waves travel over some distance.
💗1890 – Thomas Alva Edison invented fuse.
💗1897 – Karl Ferdinand Braun invented cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO).
💗1901 – Guglielmo Marconi made first transatlantic radio broadcast.
💗1904 – John Ambrose Fleming invented diode.
💗1906 – Lee de Forest invented triode.
💗1912 – Edwin Howard Armstrong developed Electronic oscillator.
💗1928 – First experimental Television broadcast in the US.
💗1929 – First public TV broadcast in Germany.
💗1941 – Konrad Zuse developed the first programmable computer.
💗1943 – Eisler invented the Printed Circuit Board.
💗1944 – John Logie Baird developed the first color picture tube.
💗1958 – Jack Kilby invented the integrated circuit (IC).
💗1960 – Theodore Harold Maiman invented the Laser.
💗1962 – Nick Holonyak Jr. invented the LED.
💗1962 – Hofstein, Heiman, and RCA invented MOSFET Transistors.
💗1964 – Kemeny and Kurtz introduced the BASIC programming language.
💗1970 – INTEL introduced the first Microprocessor.
💗1973 – John F. Mitchell and Dr. Martin Cooper of Motorola invented the first mobile phone.
💗2007 – Apple introduced the first iPhone.
WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF ELECTRONICS?
We are now living in the age of electronics. Electronics are tied into so many different aspects of our life. It is hard to find an electrical item in your home that does not have electronics partnered with it, in some way. Most of us begin our day by waking up to an electronic alarm clock. I sometimes wonder what time we would wake up without it. In addition, one of your first stops in the morning will be at your coffee maker. Another electronic contraption. Then you stroll over to the television set and turn on another electronic device. I know that I cannot start my day without a cup of coffee. I just don’t function yet. Millions of people in the world every day, depend on the television set for news and entertainment.
IMPORTANCE OF ELECTRONICS IN OUR LIFE
Electronics play a big part in our every day lives. Even if we do not realize it, just about everywhere we go and everything we do they have become integrated with our lifestyle.With the advent of iPad, iPad and iPhone, electronics seems to become part and parcel of our lives. From computers to music and home appliances, electronics have become a necessity.
CAREERS IN
TECH: WOMEN AND DIVERSITY
What
is it like to have a career in technology and how is the industry tackling the
low number of women working in the sector?
The technology sector is perceived as predominantly male, with many women feeling tech jobs are ‘not for them’. This lack of diversity will continue to be a problem until the stereotype is challenged.
The BBC’s Women in Tech event during London Techn

“We need to reposition technology so that we see it as equal a field for women as for men.”
Womens should take part in electronics technology because off mindset sharing between man and women.
Although, mans of every culture are working marvelously in electronics field but few things need to be considered like qualities of saving and environment makes better capabilities, which only found in womens.
lunes, 29 de mayo de 2017
Training in industrial electronics typically covers
performing maintenance, installation, and repairs on electronic equipment used
for industrial purposes. Find out about the requirements of these programs, and
learn about career options, job growth and salary info for electronics
graduates.
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)